After a very prolonged keep, the La Niña climate phenomenon that’s persevered for the previous three years, contributing to excessive climate worldwide, has lastly come to an finish.
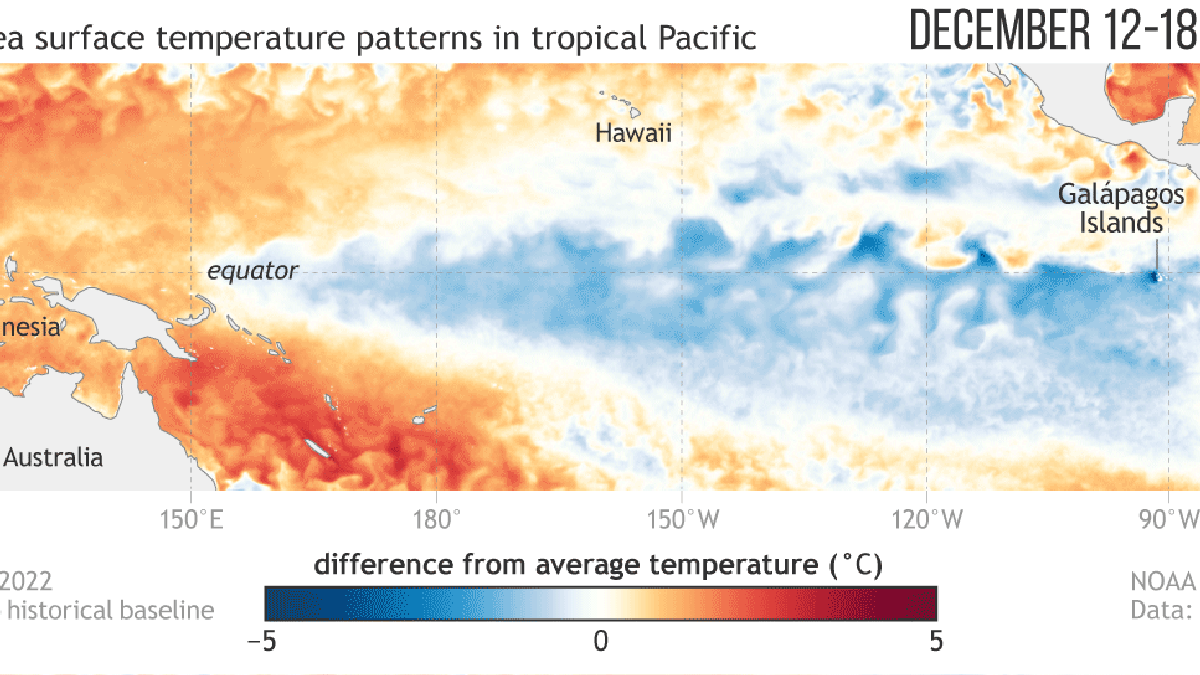
Pacific Ocean waters alongside the equator have warmed as much as near-average temps, ending the La Niña state, which is identified through Pacific sea floor temperature. The information got here in a Thursday assertion from the U.S. Local weather Prediction Heart, titled “Remaining La Niña Advisory.” Together with the marine temperature change, climatologists and meteorologists foresee a corresponding shift in a number of the climate regimes which have taken maintain over the previous few years.
La Niña is linked to a number of totally different precipitation and warmth tendencies across the planet. It contributes to drought within the southern and western U.S. and in South America, because it drives rainfall east, throughout the Pacific. Accordingly, La Niña usually means intense rains and flooding for Southeast Asia and components of Australia, as has occurred over the previous three years.
Elsewhere within the U.S., La Niña usually means extra rain (however much less snow) for the northeastern states. Furthermore, air currents dictated by ocean temperatures throughout La Niña years contribute to worse Atlantic hurricane seasons. Africa and East and Central Asia additionally really feel the phenomenon’s results.
This lately concluded La Niña occasion started in spring 2020 and have become one of the vital intense “in historic report courting again to 1950,” Michelle L’Heureux, a NOAA climatologist, instructed Axios final 12 months. Throughout the three years it lasted, it precipitated every kind of hassle. California and plenty of different western states descended deeper into an excessive drought that shrunk reservoirs to report lows, killed crops and forests, introduced on water restrictions, and extra.
G/O Media might get a fee
Concurrently, the japanese U.S. was hit by two very energetic hurricane seasons in 2020 and 2021 that resulted in a number of billion-dollar disasters, together with Hurricanes Ida and Laura. In 2020, greater than 30 storms shaped, breaking data. Although 2022’s Atlantic hurricane season was calmer, it was no cakewalk, spawning a number of devastating late-season storms, like Hurricane Ian and Hurricane Fiona.
La Niña is one facet of the ENSO (El Niño-Southern Oscillation) recurring local weather sample that shapes climate across the globe. When the ocean floor is abnormally heat within the tropical pacific, it’s referred to as an El Niño interval. When the identical waters are abnormally chilly, it’s La Niña time. When tropical Pacific waters are on par with the historic common, it’s thought of an “ENSO-neutral” situation.
And that’s the place we at present are, per NOAA and the Nationwide Climate Service: impartial territory. On the final temperature verify, the central Pacific’s sea floor temperature was simply 0.2 levels C (0.4 F) beneath the long-term common, whereas the edge for La Niña is -0.5 C, defined prediction heart researchers in a weblog put up. Throughout ENSO-neutral situations, worldwide climate is anticipated to be principally common, no matter meaning anymore. But it surely’s unclear how lengthy we’ll be staying within the impartial zone, the NOAA/NWS forecasters famous.
There’s a couple of 60% likelihood that the Pacific warms up sufficient to slingshot the world into El Niño situations by the autumn, the ENSO put up mentioned. Although, the forecasters added that predictions made within the spring are notoriously unreliable. The Local weather Prediction Heart hasn’t but instituted an official El Niño watch.
If El Niño have been to occur earlier than summer time, the U.S. may count on an abnormally gentle hurricane season. An El Niño occasion would additionally doubtless deliver moist situations to the Southwest, dry climate to some japanese states, and heat temperatures to many northern states.
The ENSO cycle is a fluctuation that happens individually from human-caused local weather change. However that doesn’t imply the 2 aren’t linked. Analysis suggests local weather change is shifting ENSO patterns, inflicting extra excessive La Niña and El Niño occasions. Local weather change may also intensify climate patterns introduced on by ENSO shifts, like heatwaves and storms.